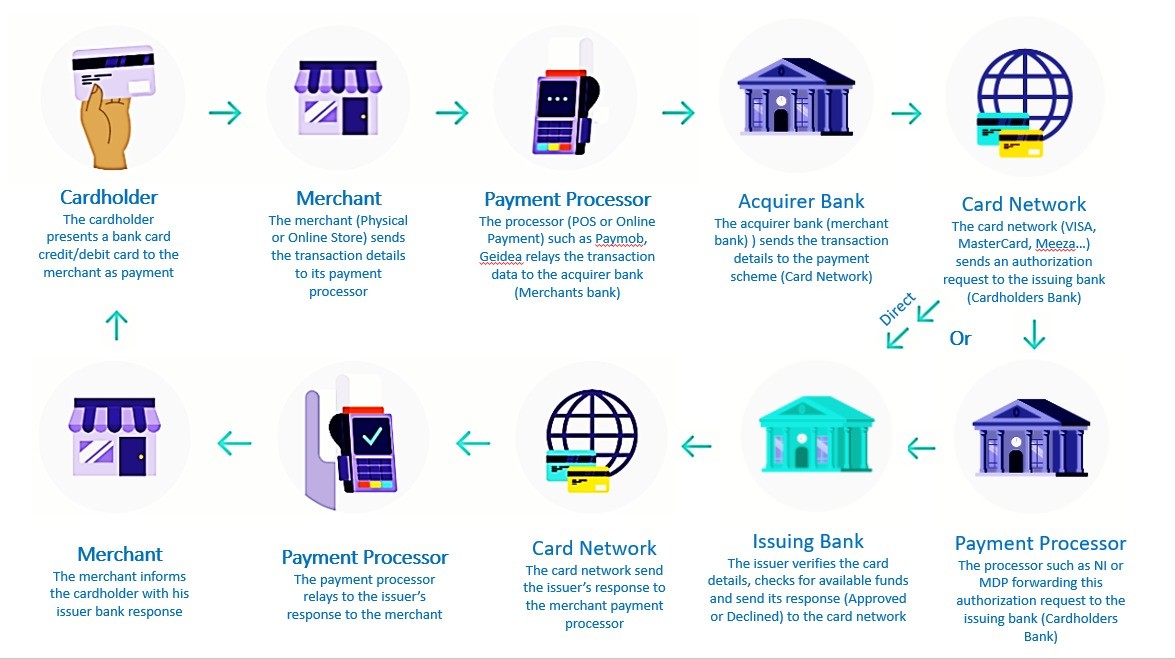
The key players in online payments
· The merchant: an online business operating in any vertical (travel, crypto, retail, eCommerce, gaming, Forex, dating, etc.), offering a product or service to customers
· The customer: the customer, also called a cardholder, who wants to access the products or services that the merchant is selling and initiates the transaction
· The issuing bank: the issuing bank is the customer’s bank that issues the cardholder’s credit or debit card on behalf of the card schemes (Visa, Mastercard)
· The acquirer: also known as the acquiring bank, the acquirer is the financial institution that maintains the merchant’s bank account (known as the merchant’s account). The acquiring bank passes the merchant’s transactions to the issuing bank to receive payment
· The payment gateway: The payment gateway facilitates the communication and transfer of data to all of the different payment providers involved in a transaction. It enables an easy, secure and smooth payment process between all parties involved.
· The payment processor: A payment processor is a vendor which businesses use to manage the logistics of accepting card payments.
· Cryptocurrency payment gateway: Cryptocurrency gateways enable you to accept digital payments and receive fiat currency immediately in exchange
How payment processing works
When a business accepts card payments, a payment processor works in the background to finalize those transactions and move money from the customer’s card account to the merchant’s account. Here’s what the process looks like:
1. A customer gives the merchant their card information. This can be at a terminal in a store, a payment page online or through another method. The information is submitted through the payment gateway, which is a payment processing portal that sometimes comes bundled with payment processing services.
2. The payment gateway sends the information to a payment processor, which initiates the transaction by sending the information to the card network, such as Mastercard or Visa, for approval.
3. The card network informs the payment processor whether the payment request is approved.
4. The merchant completes the transaction with the customer.
5. Once the transaction is complete, the payment processor informs the bank that issued the customer’s card (the issuing bank) to send funds to the merchant’s bank (the acquiring bank).
6. The merchant gets access to the funds from the sale. This can happen immediately or within a few business days, depending on the payment provider and the type of account where the funds are sent.
What is a payment gateway?
А payment gateway is the technology that captures and transfers payment data from the customer to the acquirer.
A payment gateway is what keeps the payments ecosystem rolling smoothly, as it enables online payments for consumers and businesses.
A payment gateway is a technology that captures and transfers payment data from the customer to the acquirer and then transfers the payment acceptance or decline back to the customer. A payment gateway validates the customer’s card details securely, ensures the funds are available and eventually enables merchants to get paid. It acts as an interface between a merchant’s website and its acquirer.
Through a payment gateway, a merchant can accept credit and debit cards and alternative payment methods — including digital wallets such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal, in addition to local payment methods unique to specific markets. Some PSPs provide merchant-acquiring services, making the process much easier.
In other words, the payment gateway works as the middleman between the customer and the merchant, ensuring the transaction is carried out securely and promptly. An online payment gateway can simplify how merchants integrate the necessary software. As the middleman during the payment processing, the gateway manages the customer’s sensitive card details between the acquirer and the merchant.
Payment gateways are an important feature of the digital economy. By allowing customers to safely and securely share their credit card information, these systems reduce some of the barriers to online payments.
The payment gateway facilitates the communication and transfer of data to all of the different payment providers involved in a transaction. The payment gateway also determines which payment methods are available to the customer at the time of purchase.
What is an Acquiring Bank?
The term merchant acquirer, or simply acquirer, typically refers to what is also known in the payments industry as an acquiring bank. It is a bank or other financial institution that processes credit and debit card payments for businesses.
Acquiring banks have relationships with the card networks, such as Mastercard and Visa. They enable merchants to run card transactions on the networks and accept financial responsibility for that activity. As the entities that provide access to this system, they must follow the relevant laws, regulations and card brand rules, and they perform underwriting and ongoing due diligence to ensure that their merchant customers do as well.
Example of the process:
- The acquiring bank receives card transaction details from the merchant’s payment gateway
- The acquirer bank passes these details through to the card issuer via the card scheme for authorization and completes the processing of the transaction
- The acquirer then participates in the settlement process facilitated by the card scheme
- In the end, the acquirer credits a seller’s nominated bank account with funds in accordance with the amount of the transaction between buyer and seller, as well as the acquiring agreement between the merchant and the acquirer
What is an issuing bank?
On the other side of the payment process, there’s an issuer — also known as the issuing bank. This entity is responsible for issuing cards to consumers with major card schemes such as Visa, Mastercard, and American Express.
What is a Payment Processor?
The payment processor is the entity that processes payment transactions. Processors are technology companies with the infrastructure and technical connections necessary to authorize transactions and move them from the merchant through the card networks to a consumer’s bank and back again. They also manage the process of settling the funds — moving funds from the consumer’s bank to the merchant’s bank.
In some cases, one entity can provide both functions for merchant customers. Payment processors often provide merchants with access to deposit accounts through their own relationships with acquiring banks. Acquiring banks, particularly the larger ones, sometimes offer payment processing services to their merchant clients.
Companies that offer both services are often referred to as merchant acquirers, and they eliminate the need for a merchant to identify a provider for each service.
In the payment facilitator model, individual merchants do not have direct relationships with merchant acquirers or payment processors. Having embedded payments into its own offering, the payment gateway has relationships with these entities. It then offers these services directly to the merchant, serving as a one-stop shop where a merchant can obtain everything needed to accept digital payments.
What is a cryptocurrency payment gateway?
A cryptocurrency payment gateway is a payment processor for digital currencies, similar to the payment processors, gateways, and acquiring bank credit cards. Cryptocurrency gateways enable merchants to accept digital payments and receive fiat currency immediately in exchange.
Payment Flow explained:
- The customer opts to make payment in cryptocurrency at checkout (in-store, on the web, or in-app)
- They pay the merchant an amount equal to the digital currency’s fair market value at the time of the transaction.
- The cryptocurrency payment service instantly converts the payment into the merchant’s currency, usually his local FIAT currency.
- The money is added to the account with the provider; it is deposited to the merchant’s designated bank account in intervals decided in the service contract or, depending on demand, also instant for an extra fee.
Benefits of a global payment gateway
While dealing with multiple payment providers can be an obvious hassle for any online merchant, the situation becomes even more difficult when doing business across borders.
Merchants accustomed to using off-the-shelf payment gateway technology (such as that provided via popular e-commerce software providers like Shopify, Square, and others) can often overlook the complexities of the payment world when starting out, as payments are handled out of sight and out of mind through the webshop interface. But this solution doesn’t generally scale well — and there is no way to optimize payment traffic or gain insights into how much revenue might be lost due to false payment declines and other inefficiencies.
For businesses seeking to grow and achieve scale, payments will eventually become a critical piece of the puzzle. Rather than dealing with individual providers at each link in the payment process, merchants can work with a single payment provider that consolidates all of the different payment layers under one provider.
Some of the benefits of having a global payment gateway include:
· Faster access to card products that are supported globally
· Ability to update to modern REST APIs for processing with the card schemes, resulting in cheaper development and maintenance
· Higher data quality — leading to higher approval rates and lower fraud rates
· Unified payment processing and card payment transaction data availability, which (access to the same data for all markets — e.g., issuer response codes, card schemes transaction identifiers)
· Improved service level and access to modern technology
· Business continuity thanks to the ability to route to backup processing connections
Looking for a payment gateway?
It is very important to find an efficient and reliable payment gateway. I can help you accept payments the way your business needs to. Contact us and we’ll find you the best suitable payment solution.